What are mottled teeth?
Contents
Teeth mottling refers to a condition where your teeth get spotted as a result of taking water that has so much fluorine. This happens in the course of time as teeth het calcified. In another definition, it is characterized by minute flecks or yellow or even brown spots or areas, scattered irregularly or streaked over the surface of the teeth.
Similarly, it might be taken to be a condition where the whole surface of the teeth is dead paper-white. In most cases, the surfaces are spotted with irregular, shallow pits that are normally dark in color because of the congestion of debris.
Mottled teeth condition has been found to not only affect humans but also cattle. The cattle and mostly the sheep and horses have been found to be victims of the condition, based on various studies that have been conducted far and wide.
What does a mottled skin mean?
The mottling of teeth never takes place after teeth have fully erupted. It can however take place during the times of eruption in deciduous or even permanent teeth. The condition does not necessarily affect all the teeth or all members of a family members.There have been findings that twins are likely to have same mottled areas of a similar pattern and tint, upon exactly same teeth with broadness of bands.
It is also the hypo-mineralization of dental enamel that is caused by chronic ingestion of fluoride that is above the optimal levels during the formative stages of dental hard tissues [According to Dean, 1942, WHO, 1984, Rahmatulla, 1995]. The normal levels of fluoride are 0.05 to 0.07 mg F/Kg/day and above.
Individuals at the age of one to four years are at the highest risk of contracting the condition when exposed to fluoride. The occurrence and severity of the dental condition are influenced by fluoride dose, age of individuals and the duration of exposure. The risk starts to decline gradually from age of 4 to 6 years when most permanent teeth matured.
Clinically, dental fluorosis is classified as mild, moderate and severe. In the mild forms the enamel surface is usually hard and smooth and fluorosis appears as faint white lines or streaks visible only to trained examiners under controlled examination conditions.
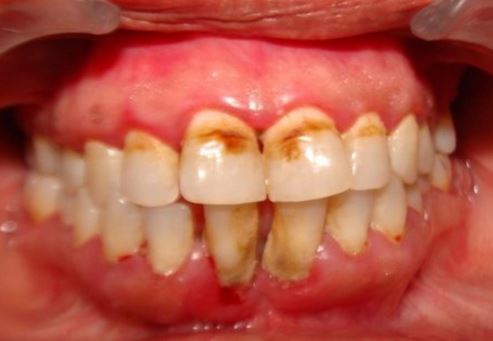
In moderate forms, dental fluorosis manifests as white mottling of teeth in which noticeable white lines or streaks have joined into larger opaque areas. Brown staining or pitting of enamel may also be present. In severe forms actual breakdown of enamel may take place with loss anatomical structure of the teeth.
The connection between fluoride and dental health began to be seriously explored in the early twentieth century. After the common cold, tooth decay is the second most common disease in the world though it is very preventable.
Mottled teeth causes
There has been observations that certain diseases at some point in teeth eruption cause certain types of true mottling. There have been similar studies that have shown that endemic areas where childhood hygienization is far below average, there is lack of general as well as oral hygiene and hence children are likely to have mottling of teeth.
The major causes of mottled teeth however is the high content of fluorine in the drinks, foods and the toothpaste that we use. The earlier exposure of your child to dental products with fluorine makes that child more susceptible to the condition. This condition that results to mottling is called fluorosis.
Fluorosis from dental products. Most toothpastes and mouth washes/ rinses which sometimes children enjoy the taste have high levels of fluoride.
In most cases, mottled teeth condition is also called dental fluorosis. Water fluorosis is brought about by excess fluorine that is found in water. Fluoride can be transferred from mother to the fetus through the placenta. In other cases, fluoride is ingested by breathing in certain contaminants in the air. When absorbed in the body, it goes in the blood stream then it is deposited into the bones.
Fluoride is a natural constituent of water. However, the levels of fluoride above the currently recommended range for drinking water may increase the risks of severe fluorosis. In the areas where the levels are more than 2 parts per million, it is recommended by CDC you take water from other sources.
Commercial products with high amounts of caffeine can also lead to mottled teeth. The high caffeine in the products causes teeth discoloration. You can change the consumption to other products that like green tea, decaffeinated coffee, white wine and light colored sodas.
Small children, in most case those younger than 6 are not able to reliably spit out when brushing. In the end result, they may end up swallowing a huge portion of the toothpaste that has been placed on the brush. If it contains fluoride, over time the enough may be ingested to an extent that fluorosis forms.
Tooth mottling in children and infants
Small children, in most case those younger than 6 are not able to reliably spit out when brushing. In the end result, they may end up swallowing a huge portion of the toothpaste that has been placed on the brush. If it contains fluoride, over time the enough may be ingested to an extent that fluorosis forms.
One to three years old may get up to 80% of their daily intake of fluoride from toothpaste. [Almeida, 2007]. In another finding, it has been shown that 2 to 3 year olds take in about 48% of the amount of toothpaste taken; 4 year’s olds 42%, 5 year olds 34% and 25% in 6 year olds.
Consumption of too much fluoride by your child can lead to the disruption of the formation of the enamel, on the outer part of the permanent teeth and thereafter result into fluorosis that will vary from minor discolorations to irregularities in teeth formation.
The good news is that the extra fluoride does not affect other parts of your infant’s teeth. That is to say, once the teeth have erupted into the mouth, they will not be at any point susceptible to fluorosis. Good still is that fluorosis is a cosmetic condition and not a disease. It can easily be detected and dealt with accordingly.
Most cases of fluorosis in young children result from the consumption of fluoride supplements or even swallowing toothpaste, or at times when the water that they drink is already fluoridated to a great extent.
There are some other factors known to cause intrinsic discoloration and they include metabolic disorders, systemic syndromes, dentin defects, tetracycline stains, fluorosis, trauma, and enamel hypoplasia.
Teeth mottling treatment
Tooth bleaching can be a good and the first step for treating certain kinds of dental staining problems. It is usually reserved for a mild, uniform, discoloration of the teeth. The bleaching is time and dose related. The bleach oxidizes the organic pigments in the tooth, breaking down the long-chain stain molecules.
The bleaching can be done at three levels:
- In office vital bleaching
- Overnight vital bleaching
- Whitening strips
Regarding the In-office vital bleach, it uses about 30-38% hydrogen peroxide that is applied directly on the teeth. A special light may also be used to speed up the whitening process. There are likely problems of teeth sensitivity and gingival irritation all the same.
Overnight vital bleach involves the use of carbamide peroxide of about 10% used in a custom tray. It is used when there are multiple discolored teeth. It is effective for yellow, orange or light brown discoloration in primary and permanent teeth. It may however result in temporary teeth sensitivity.
It is good to know that with overnight vital bleach, treatment times are as short as 2 weeks. A whitening effect will be seen after daily bleaching within two to six weeks. The shade change will be stable for 6 to 12 months, or longer. You should return to the dental office after one week for a post-operative check-up appointment.
Whitening strips also provide an alternative. They contain hydrogen peroxide of about 6.5 or 14% strength which is delivered via a thin a very flexible polythene strip. It is used for multiple discolored teeth and works slightly better on upper than the lower teeth. It however may lead to teeth sensitivity and oral tissue irritation.
Good to know still, the combination therapy of enamel micro-abrasion could provide some relief to those struggling with this condition. This is a no restorative, conservative treatment that works both chemically and mechanically to remove up to 0.2 mm of affected enamel per application.
For some patients, the depth of the staining may be beyond the scope of micro-abrasion alone. Conservatively targeting the deeper stains (without covering them with composite) can be achieved by adding Minimal Intervention (MI) Paste to the treatment sequence.
There are however other cheap, affordable and readily available remedies and those are the home remedies. They are equally good and effective. When used well as directed, they produce very desirable results.
One of the most effective and used remedy is baking soda. This is an ingredient that is not only used in baking but it can also be used to whiten teeth. You can either purchase toothpaste with baking soda incorporated in or you can formulate your own. If you make up your mind to make your own, then:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of your non-fluoride toothpaste
- Then mix it with 1 teaspoon of baking soda, then place it on your toothbrush and brush as you normally would.
Another way to use baking soda is to pour 1 tablespoon of lemon juice mixed with 1 tablespoon of baking soda. It should form a past and place it on the toothbrush for teeth cleaning. There have been several cases where utilizing baking soda has made teeth significantly whiter. Repeat this until desired outcome is met.
Apart from that, hydrogen peroxide 3% can be very useful.
- You can take 2 teaspoons of hydrogen peroxide 3% and 2 teaspoons of water and mix it thoroughly together in a cup.
- Swish it in your mouth for no more than 1 minute.
- It will become foamy which is standard.
- Then spit out and rinse mouth with water.
- Repeat this process daily until improvements prevail.
- Make sure that the peroxide is 3% due to accidental consumption purposes
Apart from the above solutions, certain fruits and vegetables are really good for your teeth. Some of the most common fruits to eat for teeth are carrots, celery, and apples. These are high in Vitamin C which kills bacteria and they produce more saliva which helps to remove plague. Some foods to avoid are anything acidic like tomato sauces, pickles, balsamic vinegar and oranges. Even soy sauce has been proven to turn teeth coloration
Over and above, it is always good to prevent than come to cure later on. There are tips you ought to take in as a daily practice in your schedule as you take care of your teeth. First of all, you should exhibit high levels of teeth hygiene, both for you and your child or infant.
Apart from that, always consult your dentist before choosing toothpaste for your family and use only as much amount of it for brushing your teeth as is indicated on the instruction list appended with the toothpaste. It is also advisable to keep toothpastes out of the reach of children.
It is also beneficial to increase the consumption of calcium through natural sources like milk and dairy products as well as through supplements, as this mineral helps in absorbing the excess fluoride ions. It is hence clear that it is cheaper to prevent than come to cure later on.
References and Sources